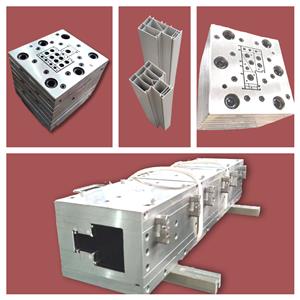
พลาสติกพีวีซี โครงสร้างแม่พิมพ์อัดรีด เผยม่านสำหรับคุณ
แม่พิมพ์ที่ใช้กันทั่วไปมีสองรูปแบบ: แม่พิมพ์แบบขั้นบันไดและแม่พิมพ์ไล่ระดับแบบตัดขวาง เส้นทางการไหลของแม่พิมพ์ขั้นบันไดจะเปลี่ยนไปเป็นขั้นตอน ซึ่งทำจากเทมเพลตปากหลายอันที่เชื่อมต่อกันเป็นชุด แต่ละแผ่นจะถูกกลึงให้เป็นรูปทรงที่สอดคล้องกัน ซึ่งจะค่อยๆ เปลี่ยนจากรูปทรงกลมของทางเข้าไปเป็นรูปทรงทางออกที่ต้องการ มีมุมเอียงที่ทางเข้าของแต่ละบล็อกเพื่อให้การเปลี่ยนจากรูปร่างหนึ่งไปอีกรูปร่างหนึ่งสมบูรณ์ ต้นทุนการประมวลผลแม่พิมพ์ชนิดนี้ต่ำ ช่องทางการไหลไม่คล่องตัวในอุดมคติ และโดยทั่วไปไม่จำเป็นต้องใช้เป็นโปรไฟล์หลัก นักวิ่งแม่พิมพ์ไล่ระดับส่วนมีความคล่องตัว ไม่มีโซนการกักเก็บวัสดุในตัววิ่ง การหลอมจะค่อยๆ และกระจายอย่างแม่นยำไปยังแต่ละส่วนของรูปทรงทางออกจากวงกลมที่ทางเข้า และความเร็วจะเพิ่มขึ้นอย่างต่อเนื่องจนถึง ความเร็วทางออกที่ต้องการและความเร็วของแต่ละจุดบนส่วนจะเท่ากัน สำหรับโปรไฟล์พลาสติก พีวีซี ที่มีแกนแม่พิมพ์ที่ซับซ้อน แกนแม่พิมพ์จะถูกรวมเข้ากับแผ่นยึด บางส่วนจะยึดเข้ากับแผ่นยึดโดยการค้นหาหมุดและสกรู และบางส่วนจะฝังอยู่บนแผ่นตัวยึดโดยการฝังแน่น ไม่สามารถถอดประกอบได้ง่ายระหว่างการใช้งาน เนื่องจากต้องใช้เวลานานในการประกอบและแก้ไขจุดบกพร่อง นอกจากนี้ การแบ่งการหลอมเหลวยังดำเนินการในสองวิธี: บนกรวยแบ่ง และในส่วนการบีบอัด แม่พิมพ์ไล่ระดับส่วนสามารถใช้เป็นแม่พิมพ์โปรไฟล์หลักได้ แม่พิมพ์อัดรีดโปรไฟล์พลาสติก พีวีซี เป็นส่วนหลักของสายการผลิตการอัดขึ้นรูปซึ่งรวมถึงปากตาย (หรือที่เรียกว่าหัวตาย) แม่พิมพ์สร้างรูปร่างถังเก็บน้ำหล่อเย็น ฯลฯ ปากตายประกอบกับหน้าแปลนบนหัวเครื่องอัดรีดด้วยวิธี ของหน้าแปลน และเชื่อมต่อวงแหวนทำความร้อน แผ่นทำความร้อน แหล่งจ่ายไฟ และเทอร์โมคัปเปิลเข้าด้วยกัน แม่พิมพ์ขึ้นรูปและถังเก็บน้ำหล่อเย็นถูกยึดไว้กับโต๊ะขึ้นรูปด้วยสกรู และเชื่อมต่อท่อน้ำและท่อแก๊ส โครงสร้างพื้นฐานของแม่พิมพ์อัดขึ้นรูปโดยทั่วไปได้รับการออกแบบให้เป็นโครงสร้างของเทมเพลตหลายชุดที่ซ้อนกันและประกอบกัน ดังนั้น ช่องการไหลของแม่พิมพ์ทั้งหมดจึงถูกสร้างขึ้นโดยการเชื่อมต่อช่องการไหลช่องใดช่องหนึ่งในแต่ละชิ้นส่วนของเทมเพลต ทั้งด้านหน้าและด้านหลัง แผ่นเพลทถูกวางตำแหน่งและยึดด้วยหมุดและโบลท์เพื่อสร้างแม่พิมพ์อัดขึ้นรูปเสาหิน สถานการณ์พื้นฐานคือ: ส่วนการไหลคงที่ของแม่พิมพ์อัดขึ้นรูปมักจะประกอบด้วยแผ่นที่มีรูพรุนและครึ่งหน้าของคอ และครึ่งหน้าและครึ่งหลังของคอก็ได้รับการออกแบบเป็นสองเทมเพลตเช่นกัน คือ คอและ แผ่นเปลี่ยนคอ นอกจากนี้ยังเป็นไปไม่ได้ที่จะไม่ใช้แผ่นที่มีรูพรุน แต่ต้องออกแบบครึ่งหน้าของช่องการไหลของคอให้เป็นช่องการไหลทรงกระบอกเพื่อรักษาเสถียรภาพของการไหล ส่วนที่แยกของแม่พิมพ์อัดขึ้นรูปเริ่มต้นจากครึ่งหลังของส่วนคอ และรวมถึงกรวยแยก แผ่นยึดแยก และแผ่นหด แผ่นหดไม่สามารถแบ่งออกเป็นแบบหล่อเดียว แต่ร่วมกับแผ่นที่เตรียมไว้ - แบบหล่อ ส่วนการขึ้นรูปของแม่พิมพ์อัดขึ้นรูปเกี่ยวข้องกับแม่แบบต่อไปนี้: แผ่นโพรง (หรือที่เรียกว่าแผ่นสำเร็จรูป) แม่แบบปาก (หรือที่เรียกว่าแผ่นขึ้นรูป) และแกน (หรือที่เรียกว่าแกนแม่พิมพ์) สำหรับแม่พิมพ์โปรไฟล์ที่เรียบง่ายกว่า แผ่นที่ขึ้นรูปสำเร็จจะถูกรวมเข้ากับแม่แบบปากให้เป็นแบบหล่อเดียว 1. ประเด็นสำคัญของการออกแบบหน้าตัดของผลิตภัณฑ์ จุดสำคัญของการออกแบบผลิตภัณฑ์โปรไฟล์พลาสติก พีวีซี คือความหนาและรูปร่างของแต่ละส่วนควรมีการกระจายแบบสมมาตร เพื่อให้การไหลของวัสดุในหัวเครื่องจักรมีความสมดุล การระบายความร้อนสามารถสม่ำเสมอ และความดันมีแนวโน้มที่จะสมดุล โดยทั่วไปแล้ว ความหนาของผนังสูงสุดและความหนาของผนังขั้นต่ำของส่วนเดียวกันจะแตกต่างกัน < 50% is appropriate. If it is a part of a closed rib, the thickness of the rib should be 20% thinner than the wall thickness. In order to avoid the stress concentration at the corner of PVC plastic profile products, the shape change of the product should be smooth and smooth transition, generally the outer corner R is not less than 0.5mm, the inner corner R is not less than 0.25mm. The hollow part of the product should not be too small. The cross-sectional shape is preferably symmetrical. 2. Structure type and design principle of mold The mold is the forming part of the extruder, which is mainly composed of neck seat, shunt cone, support plate (also known as bracket), core mold, mouth template and adjusting screw. PVC plastic profile extrusion die county is mainly composed of three sections: feeding section one by machine base and distribution cone composed of machine head flow channel feeding section, is conical: melt distribution and forming section one by support plate and mouth die compression part constitute melt distribution and forming section, the shape is gradually close to the PVC plastic profile section, parallel section mouth die and core die constitute the machine head parallel section, (1) There are two types of mold structure for extruded plastic profiles: plate head and streamlined head. According to the different methods of processing and manufacturing the machine head, the streamlined head fork is divided into integral streamlined and segmented (also known as stepped) streamlined. (2) Mold design principle The mold is the key part of PVC plastic profile extrusion, and its function is to extrude a blank similar to the profile under the action of 10~25MPa extrusion force. PVC plastic profile mold runner design principle is that the runner section should be streamlined: there is enough compression ratio and shaped length to form a certain extrusion pressure: the flow resistance balance and flow symmetry of the cross-sectional gap of each runner part of the mold. The flow channel structure of the PVC plastic profile head is generally divided into three parts: feeding, compression (also known as transition part) and forming. Generally speaking, the length of the feed part of the long runner is 1 of the length of the shaping part. About 5~2 times, the length of the compression part is about 2~3 times the length of the shaping part. The maximum cross-sectional area of the compression section is in the outlet area of the bracket. The shape of the support ribs of the bracketer. The broad one is jujube nucleus-shaped. The thin ones are long prismatic. The shape of the divergence in the front of the scaffold is that it converges at the same angle on all sides, forming a torpedo body shape. The flow rate of molten material is different in the flow channel of feeding, compression and forming, the feeding part is the smallest, the forming part is the largest, and the transition part must be in between the two and gradually increase in the direction of extrusion. The melt flow rate is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area of the runner. The roughness of the runner in the head should be Ra0. 4~0.8ym, the roughness of the mouth mold runner of the stereotyped part is higher than the roughness of the inner runner, which should be Ra0.2~0. 4μm, When the extruded billet is just exported to the die, the size of the gap is increased than the mouth die, which is called the mold release expansion, that is, the Balas effect. This effect must be considered when the pulling speed of PVC plastic profile extrusion is slow and it is cooled near the outlet of the die mold. The release mold expansion of the outlet die is usually calculated by volume, and its expansion rate is generally 1.5~2.5 times, and this value changes with different aspects of melt temperature, pressure and velocity. The wall thickness size required for PVC plastic profiles depends on the wall thickness of the appropriate extruded billet on the one hand, and the pulling speed and extrusion amount on the other hand. The thickness of the extrusion blank wall mainly depends on the size of the mouth die gap, and then depends on the plasticizing performance of the material in the extruder, extrusion pressure, extrusion temperature, material performance and expansion value. First, the standard traction shrinkage rate for general wall thickness is ≤2.5%. The gap between the mouth die and the thickness of the product are taken (0.8~0.9) 1 1